What is BLS?
Basic life support (BLS) is the primary first aid care given for the victims of life-threatening illnesses or injuries until advanced medical care (Advanced Life Support- ALS) can be given to them at a hospital.
Who can give BLS?
BLS can be given by medical professionals, nurses, paramedics, medical technicians or anyone who has underwent an authorized BLS training.
Who needs to get trained in BLS?
BLS training can help many professionals like life guards, fire fighters, police officers, teachers, day-care providers, social workers, ambulance drivers and other staffs working in public places like malls, cinema halls, amusement parks, swimming pools etc.
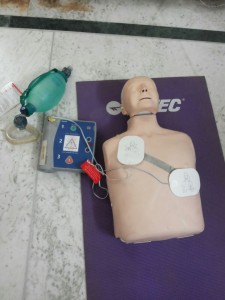
BLS is formulated for the management of medical condition such as cardiac arrest, choking and drowning. It does not involve drug usage or any other invasive skills. The usage of automated external defibrillator (AED) has provided improvement in the survival rate of victims in cardiac condition.
Basic life support promotes adequate blood circulation and proper breathing through a clear airway:
● Circulation: Ensures adequate blood supply to tissue and vital organs. Helps to deliver oxygen to all cells.
● Airway: The protection and maintenance of a clear passageway for exchange of gases (mainly oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the lungs and the atmosphere.
● Breathing: Inflation and deflation of the lungs (respiration) via the airway
The three goals of BLS are
● Circulation
● Breathing and
● Airway
These goals are formulated as ABC or CAB by the AHA (American heart association).
AIRWAY
Head- tilt/chin-tilt or jaw thrust technique is used for opening of airway.
BREATHING
The following methods can be administered to maintain the breathing of the victim.
● Mouth to mouth breathing
● Mouth to mask breathing
● Bag mask ventilation
CIRCULATION
CPR (Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation) technique is used to prevent manually the cardiac arrest with pumping action.
The above mentioned goals when achieved can help the victim to survive from any life-threatening condition and further medical care can be administered in a hospital.
GUIDELINES FOR BLS
The following changes have recently been made in the 2010 BLS guidelines.
● Make a diagnosis of cardiac arrest if a victim is unresponsive and not breathing normally.
● Look, listen and feel has been removed from the present guidelines. Just scan the chest movements
● Hands only CPR for lay rescuers and untrained rescuers.
● Rescures must place their hands in the centre of the chest, in the lower half of the sternum, rather than to spend more time using the rib margin method.
● ABC sequence changed to CABcirculation is more important than airway.
● CPR until return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) or termination of resuscitative efforts.
● High quality CPR (adequate depth of 5cms, allow recoiling, chest compressions of at least 100/min, minimize interruption, avoid hyperventilation). 30 chest compressions with 2 rescue breaths for 5 cycles in 2 mins.
● Adult AED can be used for a child or infant in case of an emergency.
● It is not necessary to use cricoid pressure during rescue breaths, when the third rescuer is available.
Chain of survival
The medical algorithm for providing basic life support to adults in the USA was published in 2005 in the journal Circulation by the American Heart Association.
The AHA uses a five-link chain of survival needed for resuscitating a collapsed victim.
● Immediate recognition of cardiac arrest and activation of the emergency response
● system.
● Early CPR with an emphasis on chest compressions.
● Rapid defibrillation.
● Effective advanced life support
● Integrated post-cardiac arrest care.
Bystanders with training in BLS can perform the first three of the four steps.
The AHA-recommended steps for resuscitation are known as DRS CAB:
● Check for Danger
● Check for a Response
● Send for help
● Cdirects rescuers to perform 30 Compressions to patients who are unresponsive and
● not breathing normally, followed by 2 rescue breaths
● Adirects rescuers to open the Airway
● Bdirects rescuers to check Breathing but no need to deliver rescue breaths
● Ddirects rescuers to attach an AED as soon as it is available and follow prompts
If the patient is unresponsive and not breathing, the responder begins CPR with chest compressions. Previously, the AHA recommended beginning CPR with rescue breaths. If responders are unwilling or unable to perform rescue breathing, they are to perform compression-only CPR, because any attempt at resuscitation is better than no attempt.
FOREIGN BODY AIRWAY OBTRUCTION (FBAO)- choking
What is FBAO?
Partial or complete blockage of breathing to the lungs due to foreign object. This can occur in both adults and in infants.
Types
● Mild airway obstruction (conscious)
● Severe airway obstruction (unconscious)
Management
● Mild airway obstruction
-Encourage the patient to continue coughing, but do nothing else.
● Severe airway obstruction
Heimlich maneuver technique can be performed to retrieve the foreign object. In case of obese /pregnant person, chest thrust is performed.
FBAO (LESS THAN 1 YEAR OLD)
Give 5 back blows and alternate with 5 chest thrusts till the foreign object comes out. In case of unconscious follow BLS algorithm.
DROWNING
Rescuers should administer CPR immediately when an unresponsive victim is removed from the water. In particular, rescue breathing is important in this situation.
A lone rescuer is advised to give CPR for a short time before leaving the victim to call emergency medical services.
Since the primary cause of cardiac arrest and death in drowning and choking victims is hypoxia, it is more important to provide rescue breathing as quickly as possible in these situations, whereas for victims of VF cardiac arrest, chest compressions and defibrillation are more important.
The knowledge about BLS encourages both medical and non-medical professionals to help in the survival of victims.